-
- Circular Linked List: A Circular list form a ring. The list is finite and each node has a successor. In a Singly Circular list the last node points to the first node. In a Doubly Circular list the first node previous points to the last node and the last node next points to the first node.
Singly Circular list
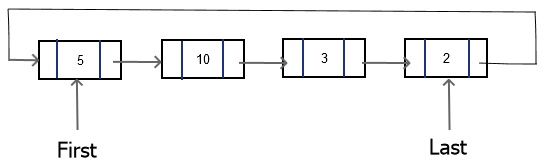
Doubly Circular list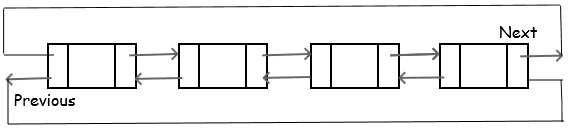
- Circular Linked List: A Circular list form a ring. The list is finite and each node has a successor. In a Singly Circular list the last node points to the first node. In a Doubly Circular list the first node previous points to the last node and the last node next points to the first node.
Java implementation of Circular Linked List
Create a Node class first which will keep info and link to the next element.
class Node {
int info;
Node next;
public Node(int value) {
this.info = value;
}
public void displayLink() {
System.out.print("[" + info + "] ");
}
}Create CircularLinkList class which will hold nodes in a circular manner.
public class CircularLinkList {
Node first;
Node last;
public CircularLinkList() {
first = null;
last = null;
}
public boolean isEmpty() {
return first == null;
}
public void insert(int value) {
Node newNode = new Node(value);
if (isEmpty()) {
first = newNode;
} else {
last.next = newNode;
}
last = newNode;
last.next = first; // last pointer points to first element
}
public boolean delete(int value) {
assert isEmpty() : "Empty list";
// if it is the first element then move first one element further
if (first.info == value) {
first = first.next;
last.next = first; // last pointer points to first element
return true;
} else {
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
while (current != last && current.info != value) {
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if (current != last) {
previous.next = current.next;
return true;
} else if (last.info == value) {
previous.next = first;
last = previous;
return true;
} else {
System.err.println("No match found in the list for value:" + value);
return false;
}
}
}
public void displayList() {
Node current = first;
Node previous = first;
while (previous != last) {
current.displayLink();
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
CircularLinkList list1 = new CircularLinkList();
list1.insert(5);
list1.insert(10);
list1.insert(15);
list1.insert(20);
System.out.println("First List-");
list1.displayList();
list1.delete(5);
System.out.println("After deleting first element 5-");
list1.displayList();
CircularLinkList list2 = new CircularLinkList();
list2.insert(5);
list2.insert(10);
list2.insert(15);
list2.insert(20);
System.out.println("Second List-");
list2.displayList();
list2.delete(20);
System.out.println("After deleting last element 20-");
list2.displayList();
CircularLinkList list3 = new CircularLinkList();
list3.insert(5);
list3.insert(10);
list3.insert(15);
list3.insert(20);
System.out.println("Third List-");
list3.displayList();
list3.delete(15);
System.out.println("After deleting middle element 15-");
list3.displayList();
}
}
Output
-------
First List-
[5] [10] [15] [20]
After deleting first element 5-
[10] [15] [20]
Second List-
[5] [10] [15] [20]
After deleting last element 20-
[5] [10] [15]
Third List-
[5] [10] [15] [20]
After deleting middle element 15-
[5] [10] [20]
All the methods are similar to singly link list only difference is that the last element will point to the first element which make difference in insert/delete at first and last position. Please refer previous page for details.
The Doubly CircularLinkList is the combination of doubly link list and circular list. It is very easy to implement. I leave the implementation as a task for the reader.
Go to the next page – Click on the below red circle with page number.
